
Penetrating trauma (e.g., gunshot or stab wounds).Blunt thoracic trauma : associated with lower rib ( 9 th–12 th ) fractures.Acceleration/deceleration injury ( automobile collisions, falls from a height): typically associated with ureteral avulsion.Complications of the genitourinary tract include urinary extravasation, urinoma, abscess formation, renal hypertension, and loss of function in the affected kidney. Treatment may be conservative or surgical depending on the severity of injury. Urethral injuries may involve the posterior urethra, causing a high-riding prostate and blood at the urethral meatus, or the anterior urethra, causing perineal pain or hematoma. Extraperitoneal bladder injuries usually resolve with catheterization, while intraperitoneal injury requires surgery, which can help to prevent peritonitis and urosepsis. Classic symptoms are gross hematuria, an inability to void, and abdominal pain. Bladder injuries are common in blunt abdominal trauma. Management may require stent placement with surgical repair. Injury to the ureters is rare and generally iatrogenic, occurring mostly during operative procedures. Mild trauma generally only requires monitoring, while high-grade injury may require emergency surgery and intensive care. The classical symptoms of renal trauma are hematuria and pain in the affected side following injury. Renal trauma is most often an acute condition caused by a blunt abdominal injury and may, if severe, represent a urological emergency. The diagnosis of genitourinary trauma typically relies on patient history, physical examination, urinalysis, and imaging (CT, cystoscopy, retrograde urethrogram). It may result in high morbidity if not properly identified and managed.
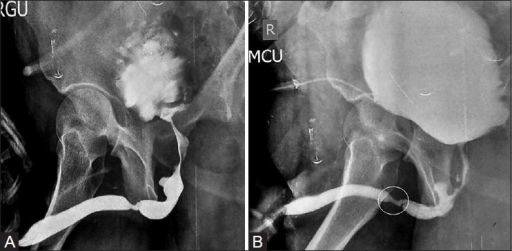
Genitourinary trauma involves injury to the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and/or urethra.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
